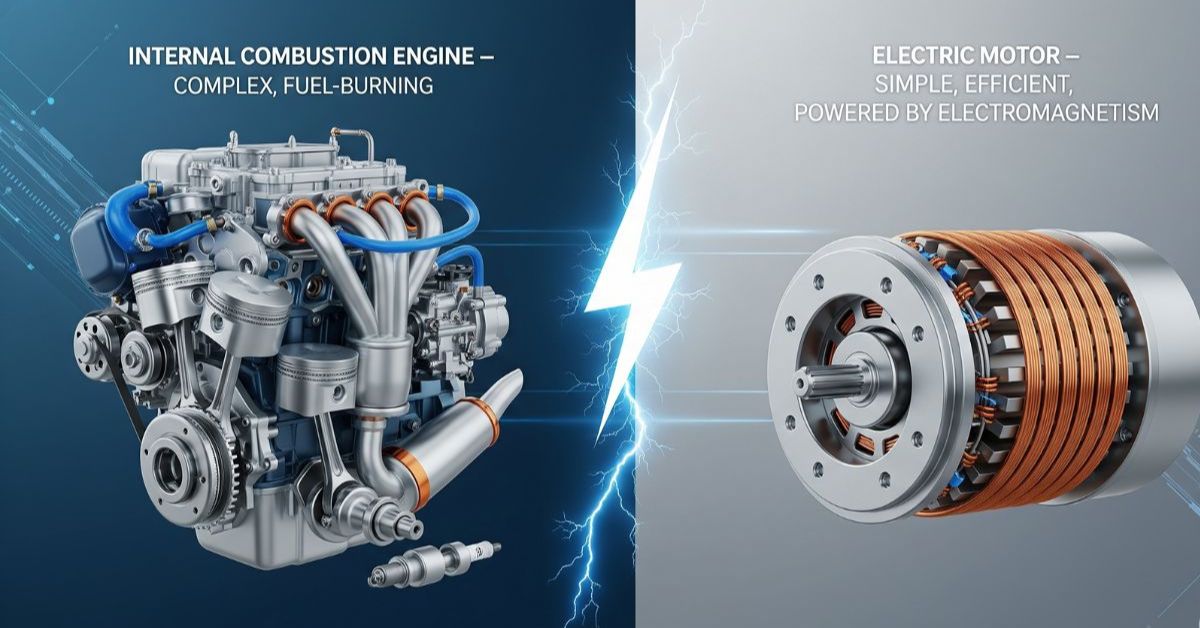
Do electric cars have engines? The short answer is no—they don’t have the traditional kind you find in gasoline or diesel cars. An “engine” usually means an internal combustion engine, which burns fuel to create motion using pistons, crankshafts, and valves. This process is noisy, less efficient, and produces emissions. Electric cars work differently—they use an electric motor powered by a battery, making them quieter, cleaner, and simpler in design.

How Electric Cars Move
Instead of an engine, electric cars run using one or more electric motors. These motors are the core of the car’s power system. Both engines and motors have the same goal—to create the spinning force that turns the wheels—but the way they do it is completely different.

An internal combustion engine works by creating controlled explosions inside its cylinders, which push pistons to turn a crankshaft. This setup is an impressive piece of engineering, but it also produces a lot of noise, heat, and exhaust fumes. It depends on many moving parts, like the cooling, exhaust, and fuel systems, all working together to keep the car running.
How an Electric Motor Works
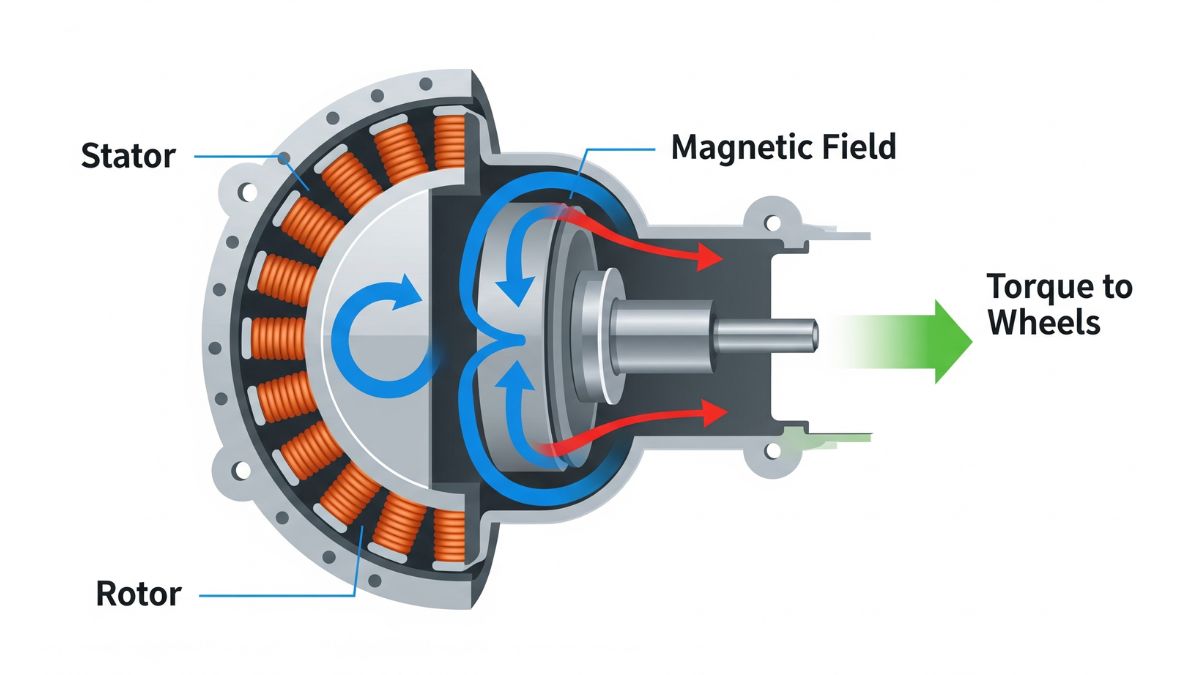
An electric motor is surprisingly simple and highly efficient. It works using the principles of electromagnetism to turn electrical energy straight into mechanical movement. Inside, it has two main parts—a stationary stator and a spinning rotor. The stator holds copper coils, and when electricity flows through them, it creates a strong magnetic field. This field pushes against the rotor’s magnetic field, making it spin. That spinning motion, called torque, is what turns the car’s wheels.
Why Electric Motors Have the Edge
Electric motors come with several big advantages. They have far fewer moving parts than a gasoline engine, which means less wear and tear, lower maintenance, and a longer lifespan. You won’t have to deal with oil changes, spark plugs, or exhaust systems in an all-electric car.
They’re also highly efficient, turning most of the battery’s energy directly into motion. In contrast, gasoline engines waste a lot of fuel energy as heat, making them much less efficient. That’s why traditional engines get very hot, while electric motors stay relatively cool.
How Electric Cars Deliver Power
One big difference between electric motors and gasoline engines is how they deliver torque. A gasoline engine needs to “rev up” to a certain speed before hitting its peak torque, which is why it uses a multi-speed transmission to stay in the best power range.
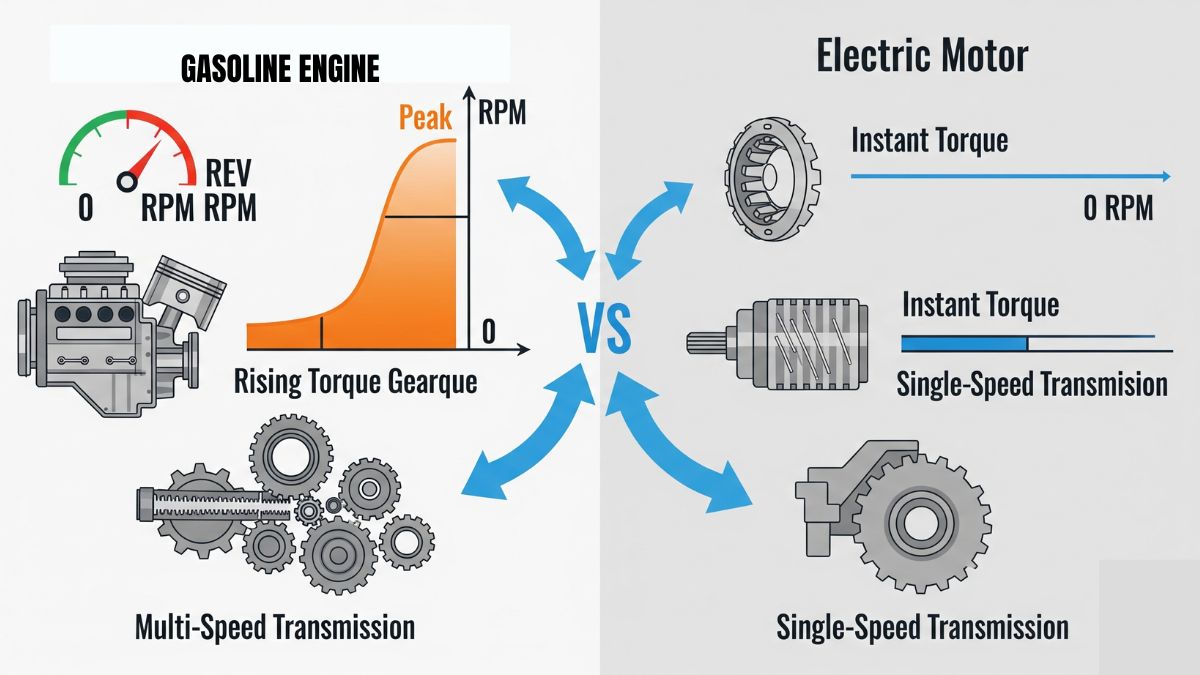
An electric motor, on the other hand, delivers full torque instantly, even from a complete stop. This is what gives electric cars their quick, thrilling acceleration. Most EVs don’t need traditional gears and run on a single-speed transmission, making the powertrain simpler—though some high-performance models may use a two-speed gearbox.
The Electric Powertrain
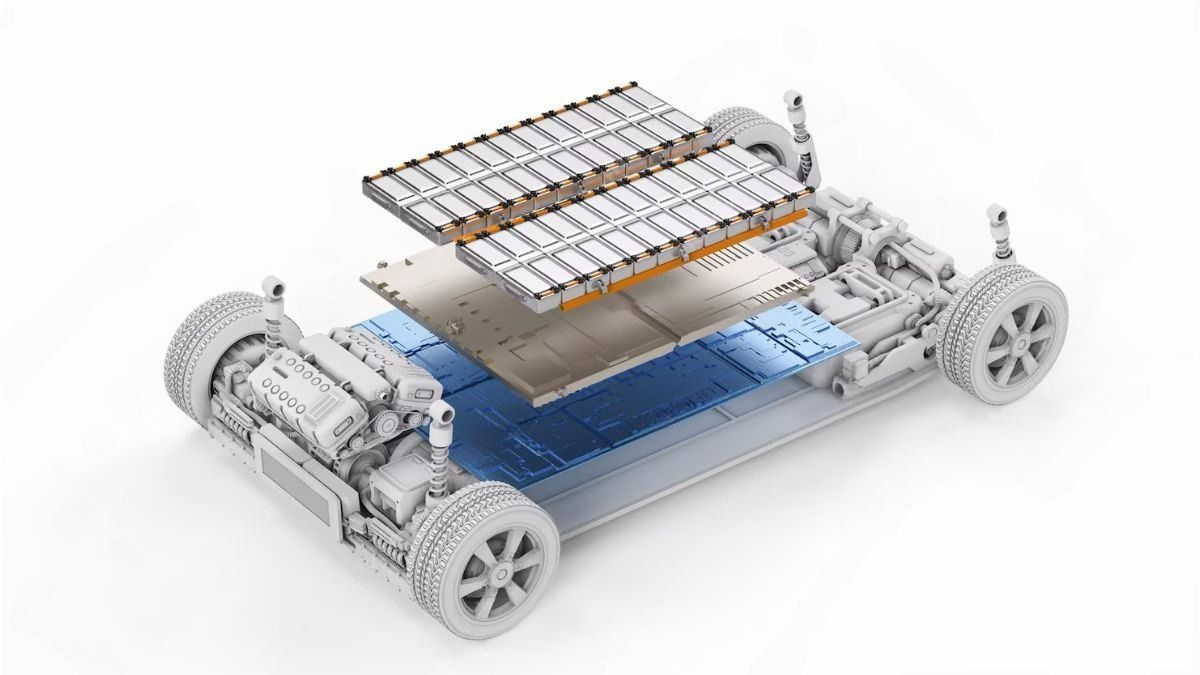
The electric motor is only one part of what makes an electric car move. The full system, called the electric powertrain, also includes a large battery pack, a power inverter, and a cooling system. The battery stores the energy needed to run the motor, while the inverter changes the battery’s direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for the motor to use. A smart power electronics controller oversees the whole process, making sure energy flows efficiently and the car performs at its best.
Engines vs. Electric Motors: A New Era
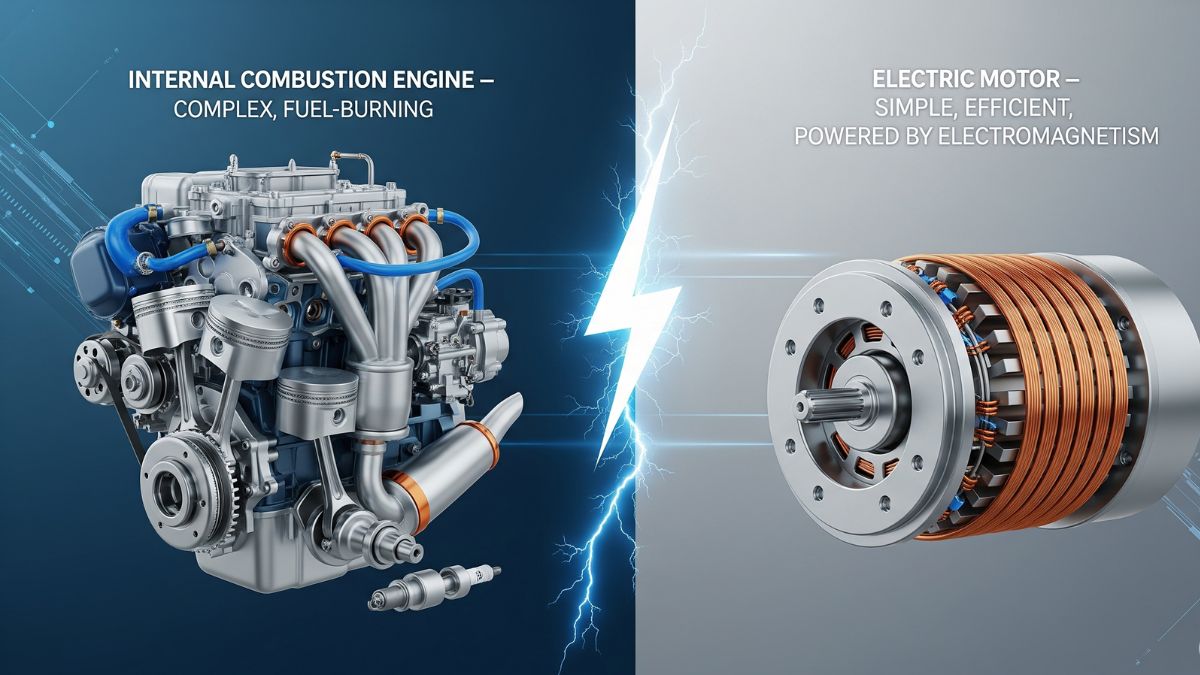
At their core, both engines and electric motors aim to do the same thing—make a car move—but the way they work is completely different. Switching from an internal combustion engine to an electric motor is a major shift in car technology, moving from a complex, fuel-burning system to a simpler, more efficient one powered by electromagnetism. So, if someone asks, “Do electric cars have engines?” you can tell them they have something far more modern and efficient—a powerful, elegant electric motor.