Many people wonder about this when thinking of switching from a regular petrol or diesel car to an electric one. The short answer is: electricity. But there’s more to it than that. In electric vehicles (EVs), electricity is stored in a big rechargeable battery and used to power an electric motor. This system works very differently from traditional cars, which burn liquid or gas fuel. Instead, EVs rely on clean, stored energy to run smoothly and efficiently.
The Heart of an Electric Car: Its Battery
The battery is the core component of an electric car. While you might know the small batteries used in gadgets like remote controls or laptops, an EV’s battery is a much bigger and more powerful version. It’s made up of thousands of small cells grouped together in a battery pack, designed to store a large amount of energy.

Most modern electric cars use lithium-ion batteries. These are popular because they can store a lot of power in a compact, lightweight form, have a long lifespan, can handle many charge cycles, and work well in different temperatures. The energy stored in this battery pack is what powers the electric motor and moves the car.
How an Electric Car Moves

When you drive an electric car, electricity from the battery goes to the electric motor, which changes it into mechanical energy to turn the wheels and move the car forward. This system is highly efficient because electric motors convert most of the energy into motion, unlike traditional engines that waste a lot as heat. This efficiency makes EVs powerful, responsive, and enjoyable to drive.
How Electricity Gets Into an Electric Car’s Battery
So, how does electricity actually get into an electric car’s battery? This is where “fueling” an EV is completely different from filling up a petrol or diesel car. Instead of going to a gas station, EV owners plug into a charging station. There are different types of chargers available, each offering different speeds and suited for different needs.
Types of Electric Car Charging
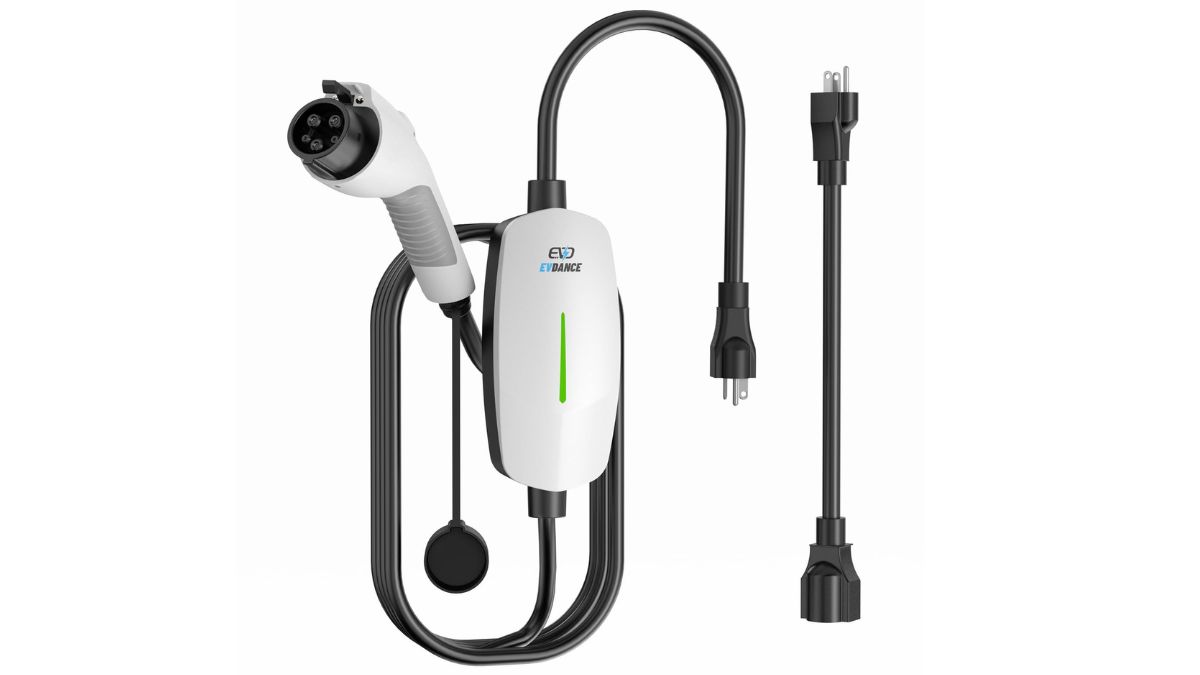

The simplest way to charge an electric car is Level 1 charging, which means plugging it into a regular household socket. It’s the slowest method, adding only a little range each hour, so it’s mainly used for overnight charging at home.
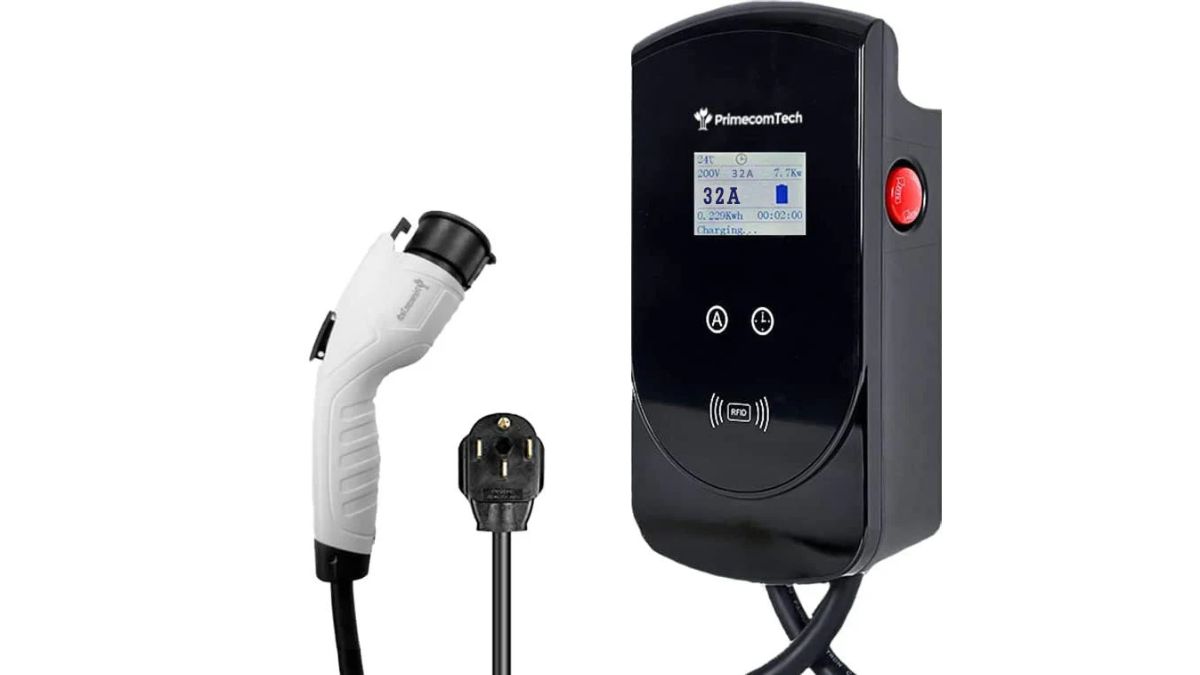

For faster charging at home, many EV owners use a Level 2 charger. This runs on a higher-voltage connection, similar to what big appliances like ovens or dryers use. It can fully charge the battery overnight and is a convenient choice for everyday use.
When you’re out and need a quick recharge, DC fast charging stations are the go-to. They work like gas stations for EVs, sending direct current (DC) straight to the battery instead of going through the car’s onboard converter. This makes charging much faster, often adding a big chunk of range in less than an hour—perfect for long trips.
Regenerative Braking: Charging While You Drive
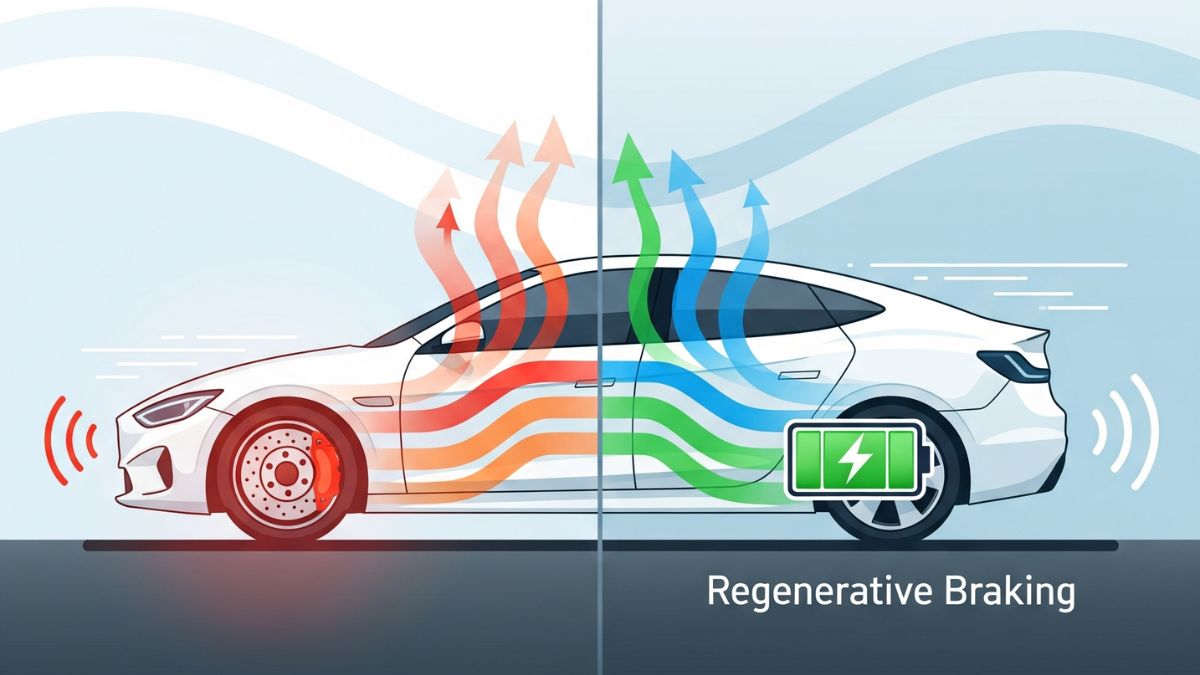
Electric cars also have a smart way of “refueling” called regenerative braking. When you lift your foot off the accelerator or press the brake, the electric motor switches roles and works like a generator. It captures energy that would normally be lost as heat and turns it back into electricity, sending it to the battery. This clever system helps extend the car’s range and makes it more efficient.
Where Electric Car Power Comes From

Electricity for EVs can come from many sources—natural gas, coal, nuclear power, or renewable energy like solar, wind, and hydroelectric dams. The environmental impact of driving an electric car depends on the energy mix in the area where it’s charged. As more regions shift to renewable energy, the benefits of EVs will keep increasing. Unlike fuel you pour into a tank, an electric car’s “fuel” is a stream of electrons that powers a clean, efficient, and high-tech way of getting around.

